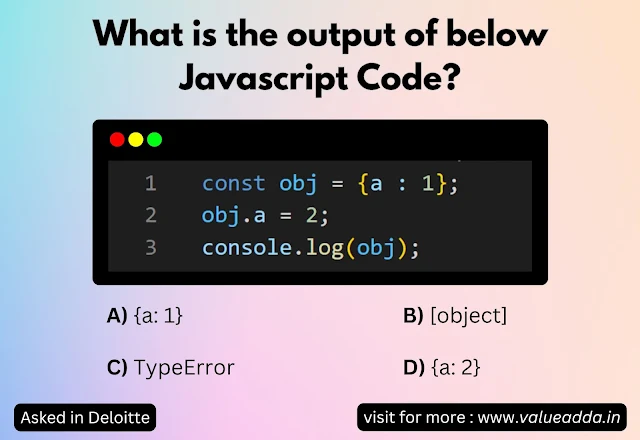
Lets explain the Code:
Step 1: Declare the Object
constKeyword:- In JavaScript,
constmeans the reference to the variable cannot be changed. - But it does not make the object immutable.
- You can still change the properties inside the object.
- What is Happening Here?
- You are declaring a constant variable named
obj. - You are assigning it an object with one property:
- This creates a reference in memory pointing to that object.
Step 2: Modify the Property
- You are not changing the reference to the object.
- You are just modifying the value of property
ainside the same object. - This is allowed even though the object was declared with
const.
Important:
- If you try to reassign the whole object like this:
This is not allowed because you cannot change the reference of a
constvariable.
- But updating existing properties:
This is completely valid.
Step 3: Log the Object
- This will print the current state of the object to the console.
- Output:
Why This Works:
-
In JavaScript,
constonly freezes the binding (the link between the variable and the object), not the object’s contents. - Objects in JavaScript are mutable by default.
- If you want to make the object truly immutable, you would have to use:
But even that only works at the top level (it’s shallow).
Quick Summary:
| Step | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Declare const obj = {a: 1} | Creates an object, reference is constant |
| 2 | Modify obj.a = 2 | Changes the property value inside the same object |
| 3 | Log the object | Prints { a: 2 } |
Key Takeaways:
const prevents reassignment, not mutation.- Objects declared with
const can still have their properties changed. - If you want an object that cannot be changed, you must use
Object.freeze.
✔ Final Answer:
D) { a: 2 }
This question appeared in the Deloitte 2nd round of interview, testing the candidate’s knowledge of const keyword with object in JavaScript.